How does an antenna work?
The antenna is a key element used to transmit or receive radio waves.
That means the antenna generates electromagnetic waves and radiates out.
The application environment, antenna manufactured material, and the performance of the antenna itself are the factors that affect the antenna.
What are the basic antenna parameters?
Many parameters affect antenna performance, such as resonance frequency, impedance, gain, aperture or radiation pattern, polarization, efficiency, and bandwidth, etc.
Those parameters could be adjusted during the antenna design process. Besides, the transmitting antenna has the maximum rated power as a considered parameter, and the receiving antenna has noise suppression parameters.
How many types of antennas are there in telecommunications?
There are many types of antennas. Common antenna types include Dipole Antenna, Monopole Antenna, Loop Antenna, Inverted F Antenna (PIFA), Patch Antenna, Microstrip antenna, array antenna (series, parallel)…etc.
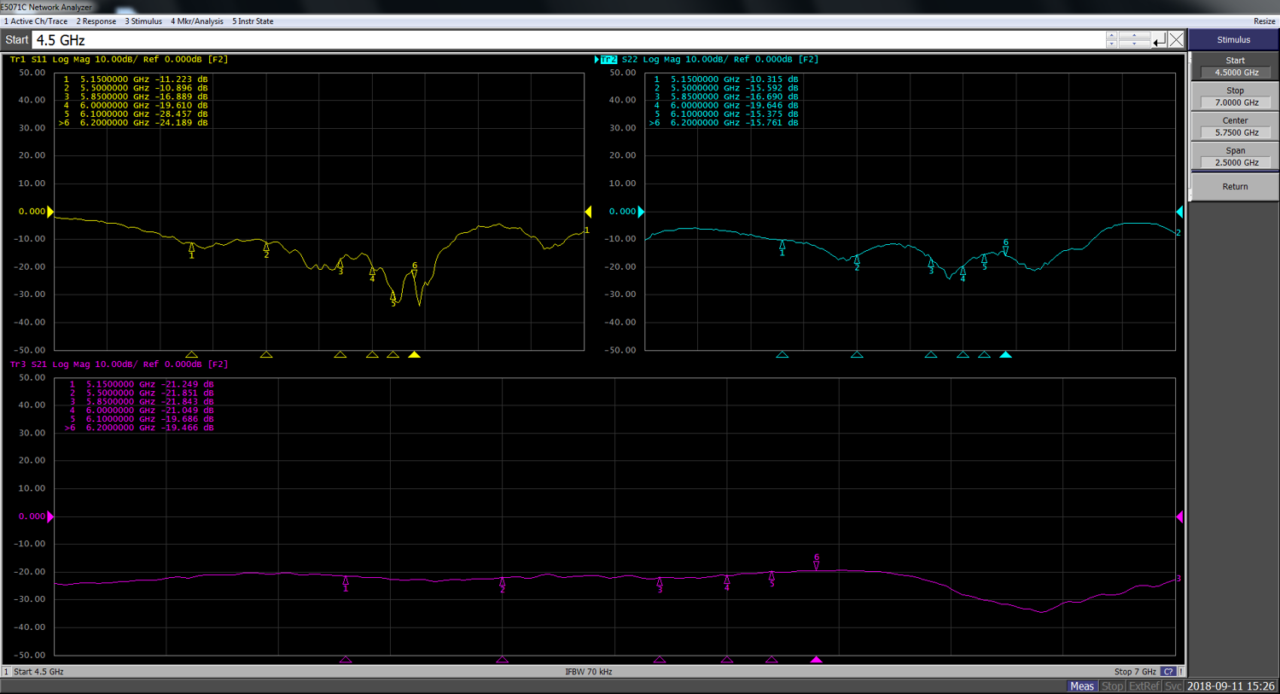
What is resonance frequency? What is the bandwidth of an antenna?
Antenna frequencies such as LTE, WI-FI, GPS, and even fifth-generation communications (5G) need to be used under standard frequencies determined by countries.
Generally speaking, the bandwidth impedance is proportional to the frequency. For example, the lower frequency has narrower bandwidth causing impedance tuning difficulty and vice versa.
Why do we use 50 ohms impedance?
50 ohms is the result of many experiments conducted by Bell Laboratories and found that the coaxial cables that are most suitable for this high-power transmission and low loss have characteristic impedances of 30 ohms and 77 ohms.
A 30-ohm coaxial cable can transmit the largest power, and a 77-ohm coaxial cable has the smallest signal loss.
The arithmetic average of 30 ohms and 77 ohm is 53.5 ohms, the geometric average of 30 ohms and 77 ohms is 48 ohms, 50 ohm is an engineering compromise between 53.5 ohms and 48 ohms.
Considering the maximum power transmission and minimum loss at the same time as much as possible, the port impedance of the half-wavelength dipole antenna and the quarter-wavelength monopole antenna are also matched, and the reflection loss caused is the smallest.
What is Antenna Efficiency?
Antenna efficiency refers to the ratio of the power radiated by the antenna (the power that effectively converts the electromagnetic wave part) to the active power input to the antenna.
Theoretically, it’s better to get a larger value, but the total value is always less than 1, and antenna placement environment, factors such as material and design need to be considered.
What is meant by the gain of an antenna?
Antenna gain is passive. In antenna design, “gain” refers to the logarithm of the ratio of the antenna radiation pattern intensity of the antenna’s strongest radiation directional to the intensity of the reference antenna.
If the reference antenna is omnidirectional, the unit of gain in dBi. For example, the gain of the dipole antenna is 2.15dBi. Dipole antennas are often used as reference antennas.
The higher the gain of the antenna, the smaller the effective angle used, and this is often forgotten. The high gain value antenna design is the power adjusted from other directions and then superimposed on the radiation in the required direction.
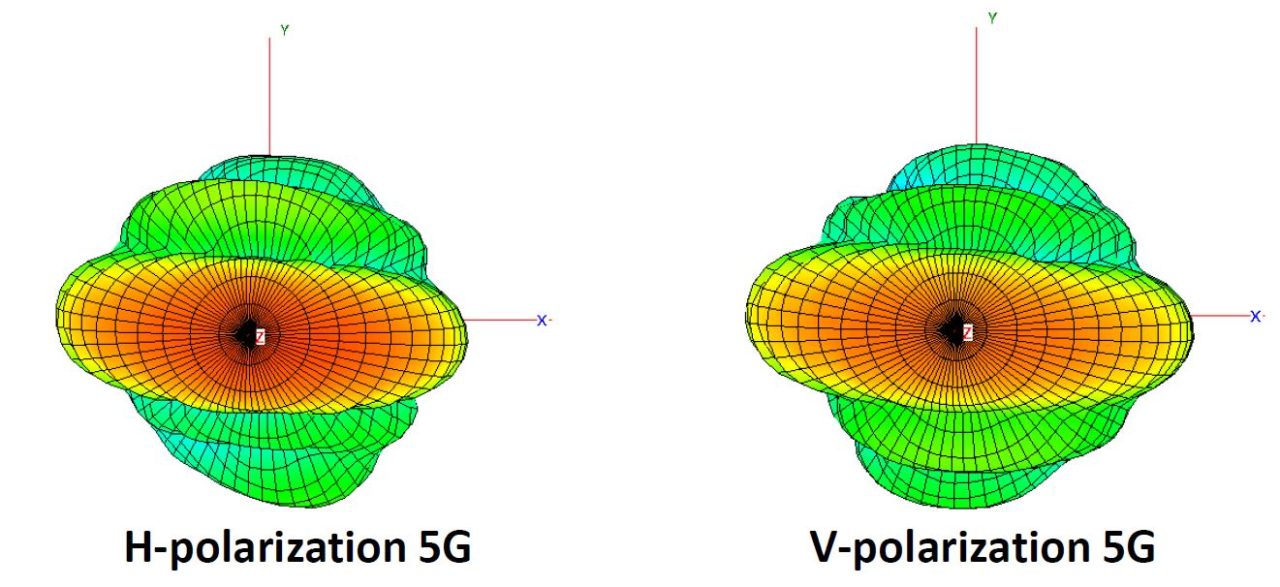
What is meant by polarization in the antenna?
When the electromagnetic wave propagates in space if the direction of the electric field vector remains fixed or rotates according to a certain rule.
This electromagnetic wave is called antenna polarization, which can be divided into horizontal polarization, vertical polarization, and 45-degree polarization.